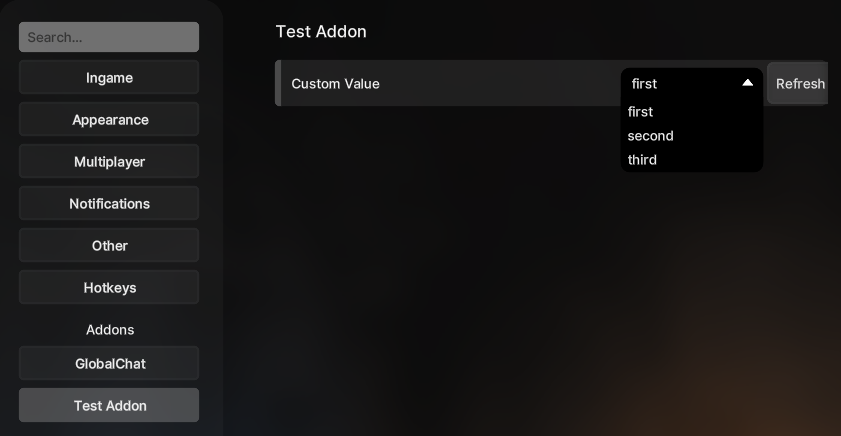
Custom Setting types
Additionally to the predefined setting types discussed in the last page, you can also create your own types to create more complex settings like the VoiceChat.
In this example we will create a custom setting widget with a Dropdown and a Button, possible use cases for this may include a list with some kind of values and a refresh button to refresh the values. The selected value shall be stored in the config.
Register Your Own Setting Type
@AutoWidget
@SettingWidget // Important to be able to use this widget in the settings
@Link("custom-setting-widget.lss")
public class CustomSettingWidget extends HorizontalListWidget {
private final String customText;
private final String initialValue;
private Consumer<String> customUpdateListener;
public CustomSettingWidget(String customText, String initialValue) {
this.customText = customText;
this.initialValue = initialValue;
}
public void setCustomUpdateListener(Consumer<String> customUpdateListener) {
this.customUpdateListener = customUpdateListener;
}
@Override
public void initialize(Parent parent) {
super.initialize(parent);
// Define your custom widget
// You can also use other methods like mouseClicked(), fileDropped(), renderWidget(), etc.
// as described earlier
DropdownWidget<String> dropdown = new DropdownWidget<>();
dropdown.addAll(new String[]{"first", "second", "third"});
dropdown.addId("custom-dropdown");
dropdown.setChangeListener(value -> {
if (this.customUpdateListener != null) {
this.customUpdateListener.accept(value);
}
});
if (this.initialValue != null) {
dropdown.setSelected(this.initialValue);
}
this.addEntry(dropdown);
ButtonWidget button = ButtonWidget.text(this.customText);
button.setPressListener(() -> {
System.out.println("Button pressed");
return true;
});
button.addId("custom-button");
this.addEntry(button);
}
@SettingElement(
// extended is optional: moves your widgets below the title of the settings
// instead of right to it, giving you more space
extended = false
)
@Target({ElementType.FIELD}) // may also be METHOD if your setting should be used on methods
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MyCustomSetting {
// Define your custom values here,
// or define none if you don't need any
String customText() default "Refresh";
}
/**
* Factory for CustomSettingWidgets, can be used in configurations via @MyCustomSetting
*/
@SettingFactory
public static class Factory implements WidgetFactory<MyCustomSetting, CustomSettingWidget> {
@Override
public Class<?>[] types() {
// The types of config values that this setting supports.
// For example in a slider this could be all numbers: PrimitiveHelper.NUMBER_PRIMITIVES
// It can also be an empty array if you don't care about the type (e.g. on a method instead of a field)
return new Class[]{String.class};
}
@Override
public CustomSettingWidget[] create(Setting setting, MyCustomSetting annotation, SettingInfo<?> info, SettingAccessor accessor) {
CustomSettingWidget customWidget = new CustomSettingWidget(
annotation.customText(), // Custom text defined in the annotation in the config
accessor.get() // Get the current value from the config
);
// When the user selects a custom value, pass it to the SettingAccessor to write it into the config
customWidget.setCustomUpdateListener(value -> accessor.set(value));
// You can also return multiple widgets here that will be placed next to each other
return new CustomSettingWidget[]{customWidget};
}
}
}
CustomSetting {
// put in your custom stylesheet here
}
@ConfigName("myaddon")
public class MyAddonConfig extends AddonConfig {
@MyCustomSetting
private final ConfigProperty<String> customValue = new ConfigProperty<>("first");
public ConfigProperty<String> customValue() {
return this.customValue;
}
}